DDR (Double Data Rate) has become a cornerstone of modern computing, offering enhanced performance and efficiency for various devices. Whether you're a tech enthusiast or a casual user, understanding DDR is essential for making informed decisions about your hardware. This article dives deep into DDR, exploring its features, benefits, and applications.
As technology evolves at an unprecedented pace, DDR continues to play a pivotal role in memory performance. From gaming rigs to data centers, DDR's influence spans across industries, driving innovation and efficiency. This guide will provide you with a detailed understanding of DDR, ensuring you stay ahead of the curve.
With this article, you'll gain insights into DDR's inner workings, its impact on performance, and how it compares to other memory technologies. By the end, you'll have a solid foundation to make smarter choices when it comes to purchasing or upgrading your hardware.
Read also:Randy Travis Health Issues A Comprehensive Overview Of His Journey
Table of Contents
- Introduction to DDR
- History of DDR
- Types of DDR
- DDR Performance
- DDR in Gaming
- DDR Compatibility
- Future of DDR
- DDR Cost Analysis
- DDR Energy Efficiency
- Conclusion
Introduction to DDR
DDR, or Double Data Rate, is a type of synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) used in computers and other electronic devices. It transfers data on both the rising and falling edges of the clock signal, effectively doubling the data rate compared to single data rate (SDR) memory. This innovation has significantly improved the speed and efficiency of memory operations.
DDR technology has undergone several iterations, each bringing significant improvements in speed, capacity, and energy efficiency. Understanding the basics of DDR is crucial for anyone looking to optimize their computing experience.
As we delve deeper into the world of DDR, we'll explore its evolution, functionality, and impact on modern technology.
History of DDR
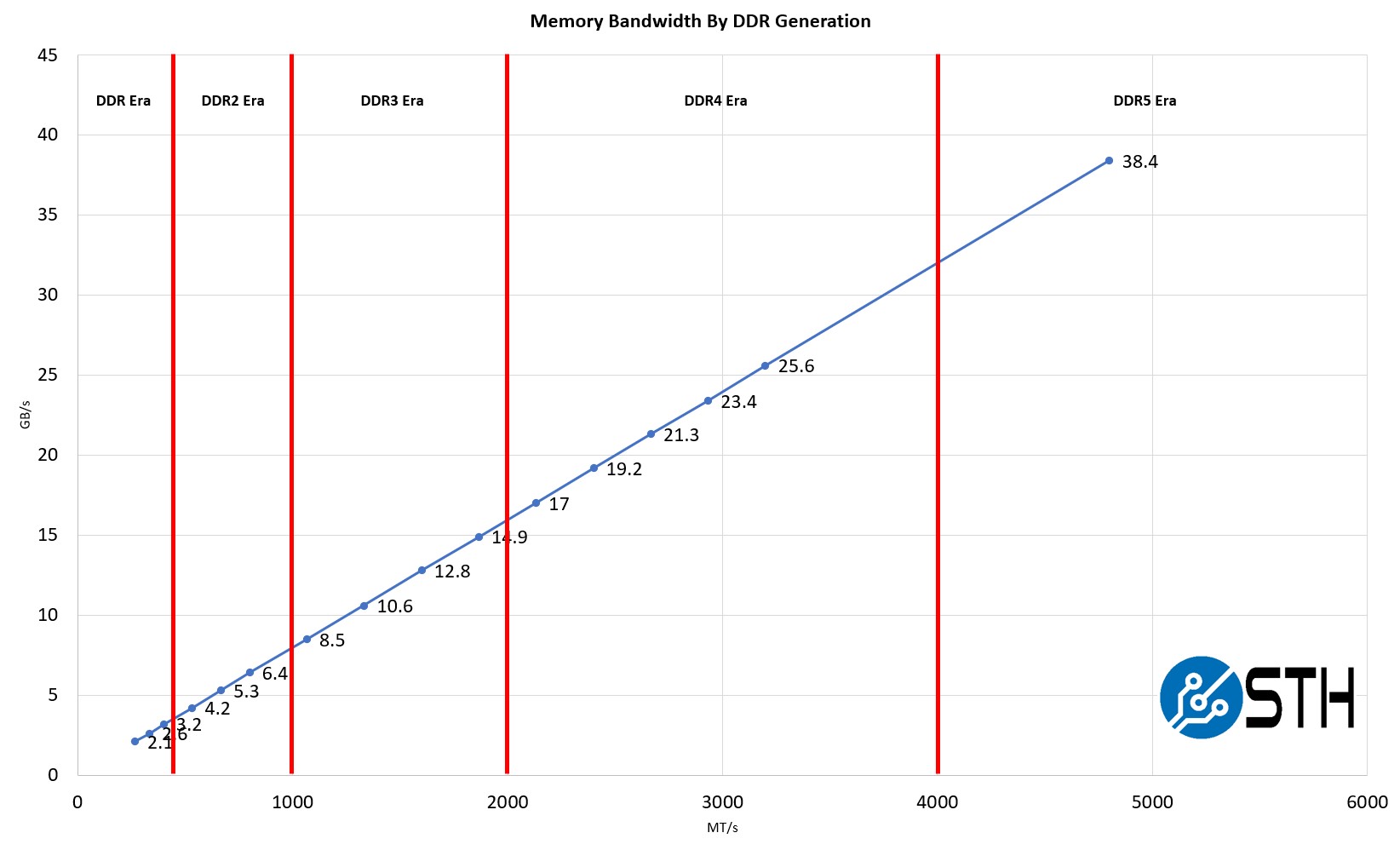
The journey of DDR began in the late 1990s when the first generation, DDR1, was introduced. Since then, DDR has evolved through multiple generations, each offering improved performance and features. Here's a brief overview of the history of DDR:
- DDR1 (2000): The first generation of DDR, featuring speeds ranging from 200 MT/s to 400 MT/s.
- DDR2 (2003): Introduced higher speeds and lower power consumption, with speeds ranging from 400 MT/s to 800 MT/s.
- DDR3 (2007): Offered even greater speeds and power efficiency, with speeds ranging from 800 MT/s to 2133 MT/s.
- DDR4 (2014): Brought significant improvements in speed, capacity, and energy efficiency, with speeds ranging from 2133 MT/s to 3200 MT/s.
- DDR5 (2020): The latest generation, featuring speeds exceeding 4800 MT/s and enhanced power management.
Each generation of DDR has contributed to the advancement of computing technology, enabling faster and more efficient systems.
Types of DDR
DDR1
DDR1 was the first iteration of DDR technology, laying the foundation for future advancements. It introduced the concept of double data rate, significantly improving memory performance compared to its predecessor, SDR.
Read also:Understanding 3rd Molar Roots A Comprehensive Guide
DDR2
Building on the success of DDR1, DDR2 brought higher speeds and lower power consumption. It featured a 4-bit prefetch buffer, allowing for faster data transfer rates.
DDR3
DDR3 further enhanced performance with increased speed and capacity. Its 8-bit prefetch buffer and improved power management made it a popular choice for many applications.
DDR4
DDR4 marked a significant leap in DDR technology, offering speeds up to 3200 MT/s and improved energy efficiency. It became the standard for modern computing systems.
DDR5
The latest generation, DDR5, pushes the boundaries of memory performance with speeds exceeding 4800 MT/s. Its advanced features, such as on-die error correction and enhanced channel architecture, make it ideal for high-performance applications.
DDR Performance
The performance of DDR memory is influenced by several factors, including speed, capacity, and latency. Faster speeds allow for quicker data transfer, while higher capacities enable systems to handle larger workloads. Latency, measured in CAS latency (CL), affects the time it takes for memory to respond to a request.
According to a study by Semantic Scholar, DDR5 offers up to 50% higher bandwidth compared to DDR4, making it an ideal choice for demanding applications such as AI and machine learning.
By understanding these factors, users can make informed decisions when selecting DDR memory for their systems.
DDR in Gaming
Gaming is one of the most demanding applications for DDR memory. High-speed DDR memory ensures smooth gameplay by reducing lag and improving frame rates. DDR5, with its superior bandwidth and capacity, is particularly well-suited for modern gaming systems.
According to NVIDIA, systems equipped with DDR5 memory can achieve up to 25% higher frame rates compared to those with DDR4. This improvement is especially noticeable in games with complex graphics and large textures.
For gamers, investing in high-performance DDR memory can significantly enhance their gaming experience.
DDR Compatibility
When upgrading or building a new system, ensuring compatibility between DDR memory and the motherboard is crucial. Each generation of DDR has different physical and electrical specifications, making it incompatible with previous generations.
For example, DDR4 memory cannot be used in a DDR3 motherboard due to differences in keying and voltage requirements. Users should carefully check the specifications of their motherboard and select compatible DDR memory.
By selecting the right DDR memory, users can ensure optimal performance and avoid compatibility issues.
Future of DDR
The future of DDR looks promising, with ongoing research and development aimed at improving performance and efficiency. Emerging technologies such as DDR6 and HBM (High Bandwidth Memory) are expected to push the boundaries of memory technology even further.
According to IEEE, future DDR generations may feature even higher speeds, lower power consumption, and advanced features such as on-die error correction and enhanced security.
As technology continues to evolve, DDR will remain a critical component of modern computing systems, driving innovation and efficiency.
DDR Cost Analysis
The cost of DDR memory varies depending on factors such as generation, capacity, and speed. Generally, newer generations of DDR memory are more expensive due to their advanced features and higher performance. However, as technology matures, prices tend to decrease.
For example, DDR5 memory is currently more expensive than DDR4, but as adoption increases, prices are expected to drop. Users should consider their budget and performance requirements when selecting DDR memory.
By balancing cost and performance, users can make cost-effective choices when purchasing DDR memory.
DDR Energy Efficiency
Energy efficiency is a critical factor in modern computing, especially for mobile devices and data centers. DDR memory has made significant strides in reducing power consumption while maintaining high performance.
DDR5, for instance, operates at a lower voltage of 1.1V compared to DDR4's 1.2V, resulting in reduced power consumption. This improvement is particularly beneficial for battery-powered devices, extending their battery life.
As energy efficiency becomes increasingly important, DDR technology will continue to play a vital role in reducing the environmental impact of computing systems.
Conclusion
In conclusion, DDR technology has revolutionized memory performance, offering faster speeds, higher capacities, and improved energy efficiency. From its humble beginnings with DDR1 to the latest generation, DDR5, each iteration has brought significant advancements to the computing world.
Understanding DDR and its impact on performance is essential for making informed decisions about hardware upgrades and purchases. By selecting the right DDR memory, users can optimize their systems for various applications, from gaming to data processing.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with DDR in the comments below. Additionally, explore our other articles for more insights into the world of technology. Thank you for reading!